While it may not get as much attention as other vitamins, a vitamin K deficiency can lead to serious health problems, such as an increased risk of bleeding and other complications.
According to Dr. Vachan S. Hukkeri, Consultant - Liver Transplant and HPB Surgery, Aster CMI Hospital, Bengaluru (India), vitamin K promotes the synthesis of clotting factors, such as prothrombin, which is necessary for the formation of blood clots to prevent excessive bleeding.
This deficiency can result from many factors, including inadequate diet, certain medical conditions, or the use of certain medications that affect vitamin K absorption.
Common symptoms of vitamin K deficiency
Vitamin K deficiency can cause a variety of symptoms, including:
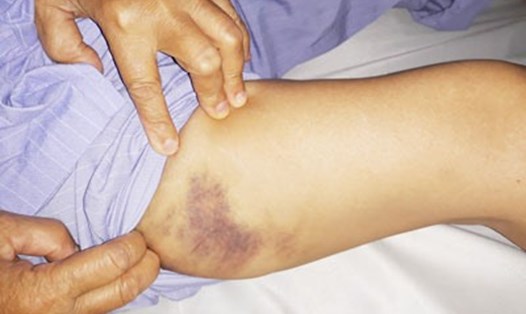
- Easy bruising.
- Cuts or wounds take longer to stop bleeding.
- Unusual bleeding from the gums or nose.
- Blood in urine or stool.
- Bone health problems, such as a higher risk of fractures due to reduced bone density.
Who is at higher risk of vitamin K deficiency?
Older adults often have poorer nutrient absorption, which can lead to deficiencies, and people with digestive disorders may have difficulty absorbing vitamin K from their diet, further increasing their risk, says Dr. Hukkeri.
Additionally, people who take antibiotics for long periods of time may experience disruption of the intestinal microflora, which plays an important role in vitamin K synthesis.
Diet rich in vitamin K
Dietary changes are essential to prevent and control vitamin K deficiency, which can lead to serious health complications, including blood clotting disorders and poor bone density, says Dr. Hukkeri.
Adding a variety of vitamin K-rich foods to your diet, such as green leafy vegetables along with fermented products like red cabbage, beets, and apples, can significantly increase your body's vitamin K levels. Furthermore, adding healthy fats like avocado and olive oil can enhance your absorption of this important nutrient.