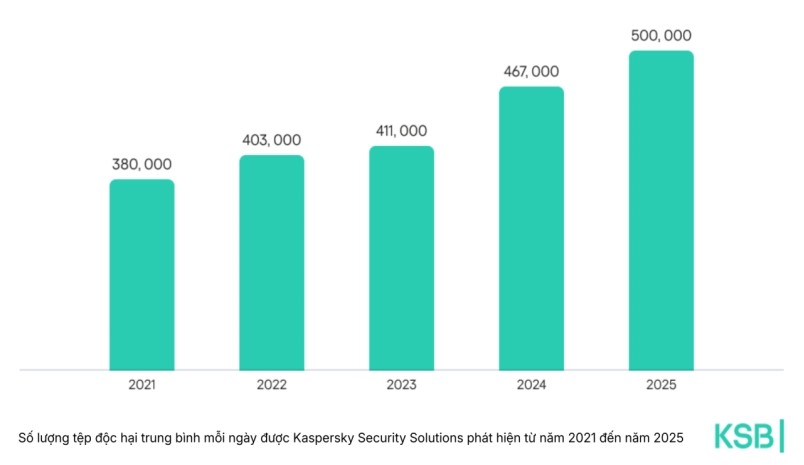
This figure increased by 7% compared to 2024. In addition, many threats are also on the rise globally, with password stealing malware increasing by 59%, sponsorship software increasing by 51%, and backdoor malware increasing by 6% compared to 2024.
Windows continues to be a top attack target. In 2025, 48% of Windows users will be targeted by many different threats. For macOS users, the rate is 29%.
27% of users globally are attacked by web threats. These are types of malware that target users when they access online.
10% of users face malware that directly penetrates the device, through USB, hard drive, CD/CD, files that penetrated the computer in compressed format (e.g. complex installation files, encrypted files...).
Data from cybersecurity experts shows that malware detected in 2025 is higher than in 2024. For example, in the Asia-Pacific region, the number of malware attacks to steal passwords increased by 132%; the number of attacks using spyware increased by 32%...
According to Alexander Liskin, Head of Threat Research at Kaspersky, the current cybersecurity landscape is shaped by increasingly sophisticated attacks targeting both organizations and individuals around the world.
Security vulnerabilities are still the most common way for attackers to attack business networks, followed by taking advantage of stolen login information. This is the reason why the number of attacks using malware to steal passwords and spyware has increased sharply this year.
To protect themselves from threats, cybersecurity experts have recommended:
For individual users:
- Do not download and install the application from unreliable sources.
- Do not click on links from strangers, emails or suspicious online advertisements.
- Always bat two-factor authentication as much as possible. Establish a strong password that includes capital, regular, digital and special characters. Use a password manager for secure storage.
- Set the update as soon as you are ready. Updates often contain patches for important vulnerabilities.
- Ignoring any requests to turn off the company's security software or security system.
- Use a comprehensive security solution, suitable for the device.
For organizations and enterprises:
- Update software regularly on all devices to avoid vulnerability exploitation and prevent attackers from breaking into internal networks.
- Do not publicize remote access services (such as RDP - Remote Desktop Protocol) on the Internet if not really necessary. If you have to use it, protect your system with a strong password and strict access control.
- Deploy advanced solutions to be able to comprehensively observe information technology infrastructure, quickly detect and handle complex threats and APT-style attacks.
- Use the latest Threat Intelligence source to promptly update the tactics, techniques and processes (TTPs) that cybercriminals are using.
- Periodically back up business data. Backup needs to be isolated from the internal network, while ensuring quick access in emergency situations.











