The 2025 Atlantic hurricane season officially began on June 1 and runs for 183 days through November 30. While storms may form outside of this time frame, only about 3% of hurricane systems form outside the regular season.
Hurricane forecasters such as the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Colorado State University, North Carolina State University and many other organizations are closely monitoring weather conditions to make forecasts on the level of storm activity.
On average, each season has 14 named storms, 7 hurricanes and 3 major storms, with a total accumulated storm energy (ACE) value of about 122. ACE is calculated based on the maximum wind speed and duration of each storm.
Looking at the 2025 typhoon season, initial forecasts show an average to above-average activity level. However, experts warn that there may be major errors in the forecast soon.
The state of the ENSO ( El Nino) phenomenon is changing and playing an important role in shaping Atlantic hurricane activity. At the end of 2024, the world will enter a La Nina period - a phenomenon often accompanied by a strong increase in storms. However, La Nina is expected to weaken by 2025, returning ENSO to a neutral state.
History shows that neutral ENSO years can lead to many different scenarios, from below-average to above-average storms, depending on factors such as sea surface temperatures, wind directions and atmospheric conditions.
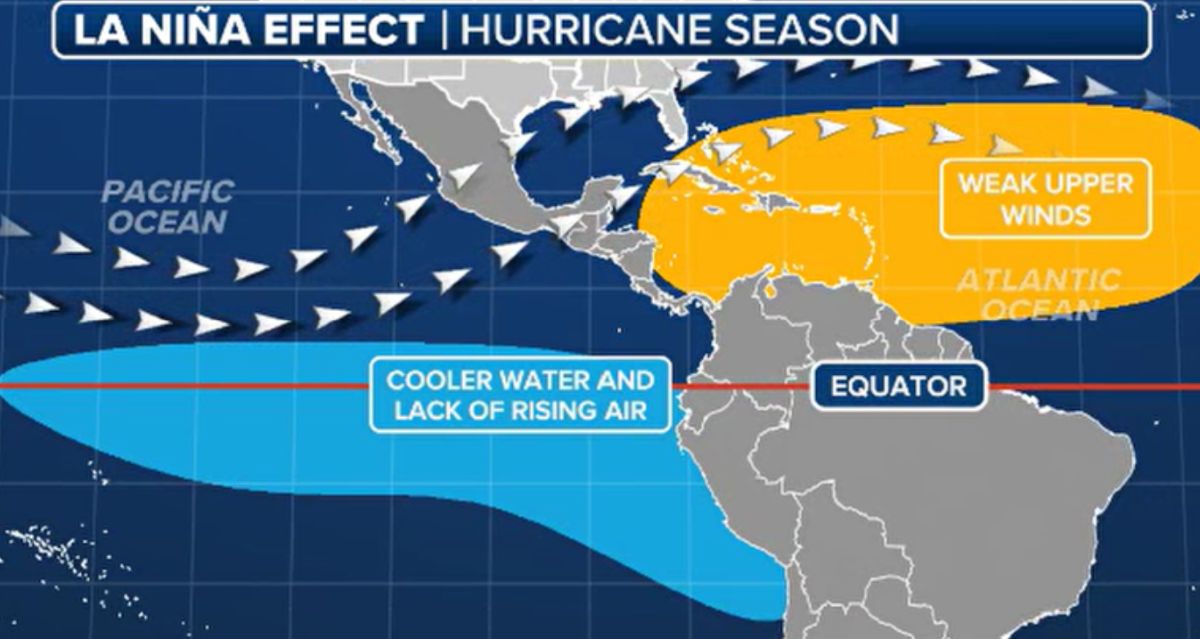
Research from Florida State University shows that during the ENSO neutral years, Florida and the Gulf of Mexico are at higher risk of being affected, similar to years with La Nina. Meanwhile, the East Coast of the US is less likely to be affected, while the Caribbean has recorded an average impact.
Weather Channel said that when sea temperatures reach about 27 degrees Celsius, the area could begin to form a storm. Currently, the Caribbean Sea is warm enough to maintain tropical activity, but there are still no signs of developing storm systems.
The Gulf of Mexico is an area to monitor closely as sea temperatures here are a few degrees above average, the Weather Channel notes. If this temperature remains in the next few months, it could facilitate the formation of a typhoon. However, the Gulf of Mexico is also vulnerable to spring cold fronts, so it is not possible to confirm for sure.
According to preliminary forecasts from Tropical Storm Risk in December last year, the 2025 hurricane season could be close to average with about 15 named storms, including seven that have reached typhoon status. Of these, three are forecast to become super typhoons of Category 3 or higher.
Meanwhile, a new study published in the NPJ Journal of Climate and Atmospheric Sciences and Climate and Atmospheric Science on February 17, 2025 showed that the number of tropical cyclones forming in the East Sea will increase significantly as El Nino moves to La Nina, especially during the cyclical La Nina period.
The frequency of storms in the East Sea is about 2.6 times higher than other La Nina transition types, mainly due to increased regional humidity, strong convergence of water vapor and the appearance of unusual atmospheric cyclones.











