Credit information (TTTD), simply understood as data, figures, and facts related to customers borrowing from credit institutions. In Vietnam, the TTTD activities of The State Bank of Vietnam (SBV) are regulated in Circular 03/2013/TT-NHNN dated January 28, 2013, specifically on the rights and responsibilities of related organizations, including the National Credit Information Center of Vietnam (CIC), a unit under the SBV, which is the focal point for TTTD activities of the SBV.
A credit score is an indicator of a borrower's creditworthiness. The score indicates the likelihood that a borrower will repay their debts and repay their loans in full and on time. A higher credit score corresponds to a lower risk of default and a higher likelihood of obtaining credit.
Each agency or organization that conducts credit scoring will have a scale corresponding to different levels of risk. At CIC, credit scores are the result of a calculation process that combines the credit information of borrowers, including identification information, information about the customer's outstanding debt, loan payment history, and some other related information.
According to CIC's individual credit scoring model, the credit score of customers is applied according to the principle of Low Rank, High Score - Low Risk Level; High Rank, Low Score - High Risk Level.
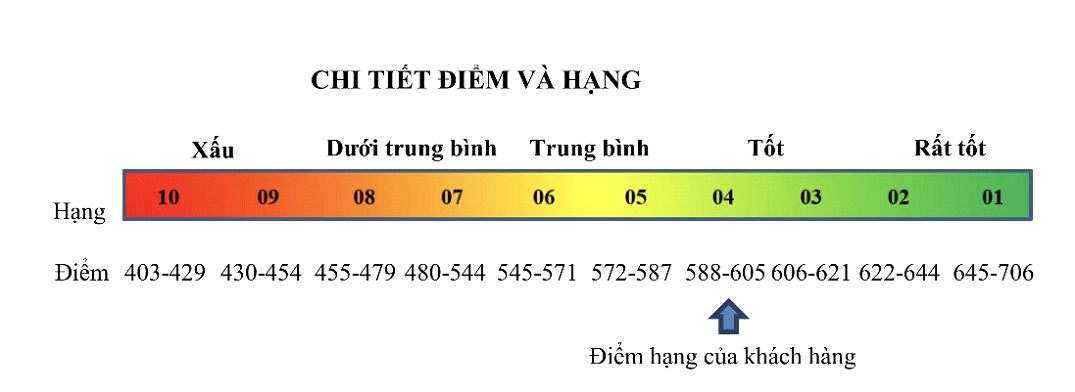
The borrower's credit score (from 403 to 706) is divided into 5 levels: Bad (rank 9, rank 10), Below average (rank 7, rank 8), Average (rank 5, rank 6), Good (rank 3, rank 4) and Very good (rank 1, rank 2), corresponding to 10 ranks from the lowest being rank 10 and the highest being rank 1.











