N.M.T (11 years old, in Hanoi) was taken by his family to a hospital in Hanoi for examination due to a khoi in the head.
The family said that in October 2024, the child touched himself and saw a brain tumor about 1.5 cm in size, leaving no pain, without any other suspicious signs. The child and her family were both very worried.
At this time, the examination of the top study area found a block about 2x1cm in size, slightly firm and painless. The ultrasound recorded a complex lesion, clear boundary, size 16mmx7mm. Blood test results were within normal limits. Doctors have diagnosed and monitored a benign fibromyalgia that has not been removed from the blood clot, so there is no intervention.
After 2 months of monitoring the child's growth, the child was re-examined and prescribed surgery to remove the entire tumor for diagnosis. After surgery to remove all the damage, the samples were sent to the pathological center for diagnosis.
The product samples that were tested for in-depth testing were pathology and immunometeorology with modern, high-tech machinery systems. After that, experts at the Medlatec Center for pathology analyzed and concluded that it was consistent with Myeloid Sarcoma.
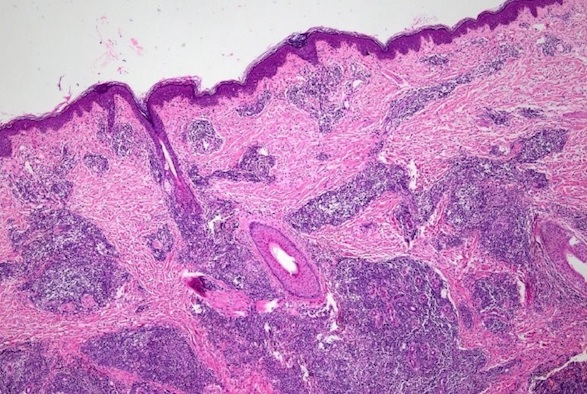
Faced with a diagnosis of myasthenia gravis, the family was very confused and decided to send the sample to consult with leading specialized hospitals such as K Hospital and the National Institute of Hematology and Blood Transfusion.
Here, pathologists also agreed and also concluded that the image of pathological tissue and immune tissue is consistent with Myeloid Sarcoma. The patient was then transferred to the National Institute of Hematology and Blood Transfusion for treatment.
According to Dr. Truong Quoc Thanh - Deputy Director of Medlatec Center for pathology, Myeloid Sarcoma is often diagnosed through methods such as:
Imaging methods such as X-ray, MRI, or CT scan determine the location and size of the tumor.
Tissue testing is a pathological test in which the cancer cells are determined through biochemistry or surgical drugs.
Immunohistochemistry when finding abnormal cells.
For cases diagnosed with Myeloid Sarcoma, depending on the severity of the patient, treatment will be prescribed with one of the following methods:
Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy to kill cancer cells in the tumor and bone marrow.
Xerotics: Can be used for tumors outside the bone marrow.
bone marrow transplantation (or stem cell transplantation): Directed in some cases if there is a recurrence or disease is progressing.
Myeloid Sarcoma (also known as mel only Sarcoma) is a rare disease, related to the formation of tumors from tienarytical cells, or myeloid cells.
This is a form of blood cancer, in which myeloid cancer cells (cells that make up red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets in bone marrow) develop into tumors outside the bone marrow, which can appear in soft tissues or organs other than bone marrow.











