In the context of the global face facing serious challenges of climate change and depletion of natural resources, the shift of energy from fossil sources to renewable energy has become an urgent and strategic task for all countries with sustainable development, including Vietnam. Vietnam is facing a great opportunity to develop green, clean energy to ensure energy security and promote sustainable economic growth (VEF, 2025).
According to the calculation of the Ministry of Industry and Trade, with the economic growth target of 8% in 2025 and a double-digit growth rate in the following years, sustainable energy transition is a key factor to ensure a stable energy supply, reduce greenhouse gas emissions and enhance Vietnam's international competitiveness (Nguyen Quynh, 2025). Vietnam's energy demand is increasing rapidly along with the rapid economic development and industrialization, strong urbanization, creating great pressure on the national power system, requiring a quick transition to renewable energy sources such as solar power, wind power and biomass to meet this demand sustainably (VEF, 2025).
The economic picture in the first quarter of 2025 shows that the service sector contributes the most to overall growth with a growth rate of 7.7%, while the processing and manufacturing industries are expected to continue to grow strongly, requiring stable and clean energy sources to maintain development momentum (Department of Statistics, 2025). The World Bank forecasts Vietnam's GDP growth in 2025 to reach about 6.8%, with the recommendation of increasing public investment in energy infrastructure and restructuring to maintain sustainable growth momentum (World Bank, 2025).
Energy transition not only helps reduce the negative impacts of climate change but also creates opportunities for the development of new industries, promotes innovation and creates jobs, especially in the fields of renewable energy equipment manufacturing and green technology. The World Bank report highlights that the development of green technologies such as electric vehicles will contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions, while creating up to 6.5 million jobs by 2050 (World Bank, 2025).
In addition, in the context of global investment flows shifting from China, Vietnam has the opportunity to attract new investment resources, especially in the fields of high technology, renewable energy and digital economy - new growth drivers that the Government pays special attention to in the economic development plan for the period 2025-2030 (Pham Thanh Binh, 2025). Promoting green energy transition combined with digital transformation will help Vietnam improve labor productivity, improve the investment environment and create a solid foundation for sustainable economic growth.
Energy transition is an inseparable key task with the goal of economic growth of 8% or more and towards double-digit growth of Vietnam in the coming years. This is not only a requirement to protect the environment but also an opportunity for Vietnam to build a green, creative, environmentally friendly economy, contributing significantly to the implementation of international commitments on emission reduction and sustainable development. The article will analyze in depth Vietnam's renewable energy potential, energy transition policies that have been and are being implemented, and point out the necessary challenges and solutions for Vietnam to maintain strong and sustainable economic growth based on a renewable energy platform.
1. Potential for renewable energy in Vietnam
Vietnam has great potential in the field of renewable energy, especially solar and wind energy. The intensity of solar radiation ranges from 2.46 to 5.77 kWh/m2/day and the average number of hours of sunshine from 1,800 to 3,000 hours/year, creating an abundant and stable source of resources for solar power development (VCA Energy, 2025). In addition to solar energy, wind energy is also a notable potential source for Vietnam. According to a report by the International Energy Organization, Vietnam's wind power potential is estimated at more than 500 GW, about 5 times higher than the country's current electricity demand (PC1EPC, 2025).
In addition, biomass energy is also an important resource that Vietnam can exploit effectively. With about 60 million tons of agricultural waste per year, a rich source of bulk materials from agriculture, forestry and urban waste can be utilized for energy production (Vietnam Zero Waste, 2023). Biomass energy not only helps to effectively treat waste and reduce environmental pollution but also provides a stable background for the national energy system, supplementing highly volatile renewable energy sources such as solar power and wind. This is an important factor in helping Vietnam diversify its energy structure and reduce dependence on fossil energy sources.
In the first quarter of 2025, renewable energy accounted for 16% of the total electricity output of the national system, with solar power reaching 6.69 billion kWh and wind power reaching 4.45 billion kWh (Lan Anh, 2025). These figures reflect the strong development of clean energy sources in Vietnam, while also demonstrating a rapid increase in recent years. The Vietnamese government has set a clear target for the near future: by 2030, the share of renewable energy will account for 32.3% of total electricity output and is expected to reach 65-70% by 2050. Along with that, solar power capacity is expected to reach 46,459 to 73,416 MW, while onshore and offshore wind power may reach more than 100,000 MW by 2050 (Thu Thao, 2025; Le Thu, 2025).
Initially, the development of the renewable energy industry has achieved positive results. By April 2025, 63 renewable energy projects had been approved for electricity prices and signed power purchase and sale (PPA) contracts, with a total capacity of more than 3,429 MW. Of these, 30 plants have been put into operation, providing more than 6 billion kWh of renewable energy (VietNam Energy, 2025). These results create a solid foundation for the renewable energy industry to develop strongly, not only providing clean electricity but also promoting the development of related industrial value chains and creating many job opportunities.
2. The importance of energy transition for economic growth
Vietnam is in the period of strong industrialization and urbanization with increased energy demand. Forecasts from the Energy Institute to 2050 show that energy demand will continue to increase sharply in key economic sectors such as agriculture, industry, trade, civil servants and transportation.
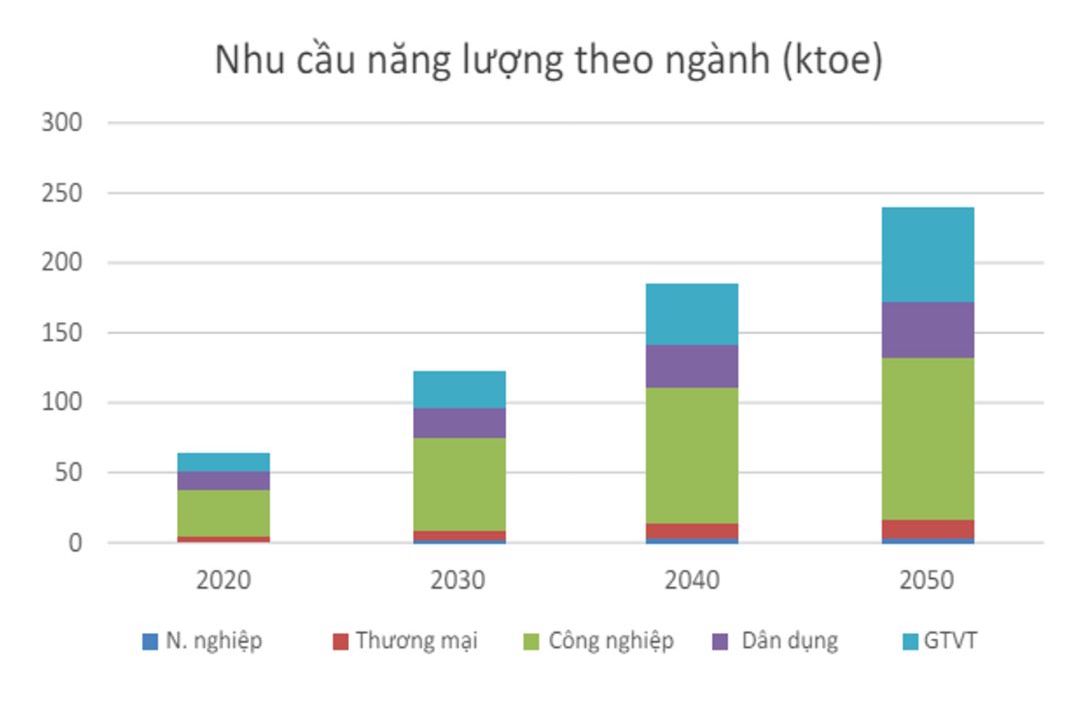
The industry, which is the pillar of the economy, is expected to account for the largest proportion of the total energy consumption, increasing from about 30 KToe in 2020 to 100 Ktoe in 2050. The expansion of industrial parks, factories, especially in areas such as construction materials, processing and heavy industry, will promote increasing energy demand. In addition, the transportation industry is also expected to grow rapidly, from 15 KToe in 2020 to nearly 90 KToe by 2050, mainly thanks to the increase in personal vehicles, expanding transport infrastructure and logistics development. These forecasts confirm the importance of energy transfer to ensure a stable supply for the economy. The development of renewable energy will help diversify the supply of energy, minimize dependence on imported fuel and minimize the volatility of energy prices, thereby protecting the economy from energy shocks and maintaining stable GDP growth.
On the other hand, energy movement also opens many opportunities to develop green industries and clean technology. As of 2024, Vietnam had 559 certified projects, far exceeding the previous target (80 green buildings in 2025 and 150 works in 2030) under the Prime Minister's Decision No. 280/QD-TTg. In particular, green industrial works account for a large proportion, up to 56.45%, with the outstanding participation of the type of factory and green warehouse. The shift to renewable energy and the application of energy -saving technology brings many benefits for businesses, especially in reducing production costs.
These technologies not only help reduce energy consumption but also reduce greenhouse gas emissions, thereby contributing to environmental protection. According to the Ministry of Industry and Trade, sustainable energy transition helps improve labor productivity and production efficiency in industries. When businesses reduce energy costs, they will be able to increase production and expand scale, thereby promoting a stable and sustainable economic development. Applying clean and efficient energy solutions will help businesses reduce cost risks and improve competitiveness in the international market.
The shift of energy to clean sources also creates a great opportunity to attract foreign investment in the renewable energy industry. Vietnam is becoming an attractive destination for international investors thanks to the abundant potential of renewable energy sources and the Government's policies to support the development of clean energy.
It is forecasted that the total investment capital for developing power sources and grids in the period of 2026 - 2050 will reach 835.4 billion USD, of which power sources account for 92.6% (773.5 billion USD) (Le Thu, 2025). The strong development of renewable energy and modern electricity infrastructure also opens up opportunities for Vietnam to strengthen regional connectivity, expand the electricity export market to neighboring countries such as Cambodia, Singapore and Malaysia. It is expected that electricity exports can reach 10,000 MW by 2035, contributing to promoting international cooperation and increasing financial resources for the economy.
3. Vietnam's major policies on energy transition
3.1. National legal framework and strategy for energy development
Recognizing the important role of renewable energy in sustainable development, energy security and environmental protection, Vietnam has provided strategic orientations for energy development to 2030 and vision to 2050 with specific goals to ensure energy security and sustainable development. This strategy focuses on increasing the ratio of renewable energy in the national energy structure, reducing the dependence on fossil energy and improving energy efficiency.
Renewable energy is increasingly playing a central role in Vietnam's national energy strategy and policies. A series of programs and policies have been implemented, especially in the field of power generation, to promote the use of clean energy sources. National Power Development Planning from V to VIII along with many incentive mechanisms have created strong momentum, helping the share of electricity from renewable sources to grow steadily, contributing to ensuring energy security and sustainable development.
The Government of Vietnam has issued a series of important policies and plannings to guide renewable energy development. Specifically, the national electricity development planning of the periods such as the VII Electrical Planning (adjustment) and the VIII Electrical Planning (PDP8) have set out a specific roadmap for the power source structure, which prioritizes the development of wind, solar power and biomass electricity. PDP8 particularly emphasizes the gradual reduction of coal power and increasing the proportion of renewable energy in the total capacity of the national electricity system.
According to the latest draft of PDP8, by 2030, the proportion of renewable energy (including wind power, solar power, and biomass power) is expected to reach 30.9.9% of total capacity and can increase to 47% if implemented in accordance with the roadmap of the Fair Energy Transition Partnership (JETP).
3.2. Preferential policies and support for renewable energy development
Financial and tax incentives
In addition to long -term plans, the Government also issues many preferential policies on finance and taxes to encourage businesses to invest in renewable energy. Wind power projects, solar power, biomass enjoy corporate income tax exemption policies for the first 4 years and decreased by 50% in the next 9 years. In addition, import taxes for machinery, equipment and vehicles serving the project are also completely exempted. In particular, the losses from the project are allowed to transfer for 5 years, helping investors have more financial rooms to overcome difficult first phase. The Government also facilitates preferential loans through Vietnam Development Bank and other financial institutions, with low interest rates and long loan periods. As a result, many energy enterprises have bravely expanded investment scale, especially in the field of wind and solar power.
Feed-in tariff price mechanism
The fixed electricity price policy (Feed-in tariff - FIT) is widely applied in the early stages of renewable energy development. FIT price ensures that investors receive a fixed electricity sale price for each kilowatt hour (kWh) of electricity produced from renewable energy sources, lasting for 20 years, creating favorable conditions for businesses to recover capital and make a profit. Although the FIT policy is gradually being replaced by a competitive bidding mechanism, the early stages of this policy have contributed to creating a strong breakthrough for the renewable electricity market.
Connection mechanism and priority mobilization
Decree 58/2025/ND-CP issued on March 3, 2025 detailing incentives for electricity prices, connection mechanisms and priority for mobilizing renewable energy with the installation of power storage systems during peak hours, helps optimize renewable energy sources and reduce pressure on the national grid.
This Decree also encourages and supports research, production, and technology transfer in the fields of wind power, solar power and storage equipment, with incentives for taxes, loans and human resource training to increase localization rates and reduce dependence on imports. The issuance of Decree 58/2025/ND-CP is considered an important step forward, creating strong motivation for investors in the renewable energy sector in Vietnam, helping to reduce financial risks and speed up project implementation (Manh Duc, 2025).
4. Challenges in energy transition
Energy shift in Vietnam, despite bringing many opportunities for green and sustainable economic development, still facing many great challenges. One of the biggest challenges today is the grid system and the ability to integrate renewable energy into the national electricity network. The current power transmission and distribution system is not capable enough to receive a large proportion of renewable energy sources such as solar power and wind power. The congestion of the transmission line, especially in the Central and the South, is limiting the ability to absorb capacity from new renewable energy projects, leading to the need to reduce renewable electricity, reduce investment efficiency and affect the goal of green energy development. In addition, energy storage technology such as battery and blue hydrogen still limits the scale and high cost, making it difficult to balance the supply and demand in the system.
The legal framework related to renewable energy in Vietnam is still lacking in consistency and not attractive enough to attract investment from economic sectors. Technical standards and regulations on renewable energy technology are not yet complete, causing difficulties in implementing renewable energy projects. Moreover, the lack of a specialized law on renewable energy reduces transparency and consistency in preferential policies, causing legal and financial risks for investors.
In addition, the initial investment cost for renewable energy projects is still very high, especially for new technologies such as offshore wind power, energy storage and green hydrogen. Clean fuel technologies have not yet competed with traditional energy sources in terms of cost, creating great pressure on the ability to mobilize capital and slow down the development of renewable energy projects.
In addition, the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic and global economic fluctuations have made investment capital more limited, while banks and investors are still cautious about the renewable energy sector due to concerns about technical and market risks.
Although Vietnam has great potential for renewable energy, it still faces dependence on fossil energy, especially imported coal and oil and gas, creating great pressure on energy security. The shortage of electricity supply due to many power plants being behind schedule, along with fluctuations in fuel prices and geopolitical risks related to imported supply, increases risks to national energy security.
Energy transition requires ensuring a stable and continuous power source, but renewable energy is highly volatile, so there is a need for intermediate power sources such as electricity to support. However, this increases operating costs and complicates the management of the national energy system.
5. Solutions to promote energy transition
To successfully implement the energy transition, Vietnam needs to deploy synchronous solutions related to technology, policies, finance and international cooperation. The goal is to overcome current challenges, while making the most of renewable energy potential, ensuring an efficient and sustainable energy transition.
The application of modern technologies and digital transformation in the energy industry is an important factor in the energy transition process. Advanced technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), smart sensors and artificial intelligence (AI) help optimize the performance of renewable power plants and smart grid systems.
Industrial data platforms and digital technology help improve the ability to forecast, manage and coordinate renewable power sources, minimize losses and increase the stability of the national power system. In addition, developing energy storage technology (such as batteries and green hydrogen) is a key factor to solve the instability of solar and wind power sources, helping to balance electricity supply and demand and improve the reliability of the national power system.
In addition to technology, perfecting the energy market policy framework and mechanism is very necessary to promote energy transition. The government needs to continue to improve and make transparent preferential policies and electricity price mechanisms, such as the FIT (Feed-in-Tariff) mechanism and the direct electricity purchase and sale contract (DPPA) model. These mechanisms will encourage the private sector to participate in investing and developing clean energy infrastructure.
At the same time, amending laws related to energy and power development planning will help facilitate the implementation of renewable energy projects, strengthen supervision and evaluation of policy implementation effectiveness, and ensure the success of energy transition.
Another important factor is investment in power grid infrastructure and energy storage systems. To solve the problem of grid congestion, especially in areas with great renewable energy potential such as the Central and Southern regions, Vietnam needs to invest in upgrading and expanding power transmission and distribution infrastructure.
The construction of large-capacity transformer stations and the application of smart grid technology will help increase the ability to connect and manage renewable power sources. Developing a large-scale power storage system will help stabilize power sources, reduce pressure on the transmission grid and support flexible operation, especially during peak hours and when renewable energy sources fluctuate.
In addition to infrastructure, creating a favorable financial mechanism and mobilizing investment resources are indispensable factors. The development of green credit packages, tax incentives, credit guarantees and long-term financial mechanisms will help reduce capital costs and attract investment in renewable energy. According to PwC's report, financial mobilization in the next 3-5 years is a decisive factor to support Vietnam's green energy transition. In addition, enhancing cooperation with international financial institutions and partners within the framework of initiatives such as JETP (Just Energy Transition Partnership) will help Vietnam access modern capital and technology, while sharing experience in managing and operating renewable energy projects.
International cooperation and technology transfer play an important role in promoting energy transition. Vietnam needs to expand cooperation with international partners such as the European Union, Japan, the United States, Canada and multilateral organizations to receive advanced technology, management experience and financial support. The construction of inter-regional renewable energy technology research and development centers, combined with high-quality human resource training, will help improve domestic capacity, reduce dependence on imported equipment and technology.
6. Conclusion
Energy transition is an important strategic factor helping Vietnam achieve the goal of sustainable economic growth. Reducing dependence on fossil energy, especially coal and oil and gas, not only protects the environment but also improves national energy security and reduces risks from international fuel price fluctuations. This is the foundation to create a stable economic environment, attract investment and develop new technology.
Develop renewable energy such as solar power, wind power and biomass to take advantage of domestic potential, diversify energy sources, and enhance competitiveness in the context of international integration. At the same time, this is an important part of Vietnam's international commitment to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and achieve the NetZero target by 2050.
However, Vietnam needs to overcome challenges in infrastructure, legal framework, investment costs and finance to effectively realize energy transition. Synchronizing solutions on technology, policies and international cooperation is a decisive factor in the success of this process.












