Update USD exchange rates of Vietcombank, Agribank, BIDV, VietinBank today
At 9:30 a.m. on November 29, the State Bank announced the central exchange rate of the Vietnamese Dong against the USD decreased by 20 VND, standing at 24,251 VND.
The reference USD exchange rate at the State Bank of Vietnam (buying - selling) remains unchanged, currently at: 23,400 VND - 25,450 VND.
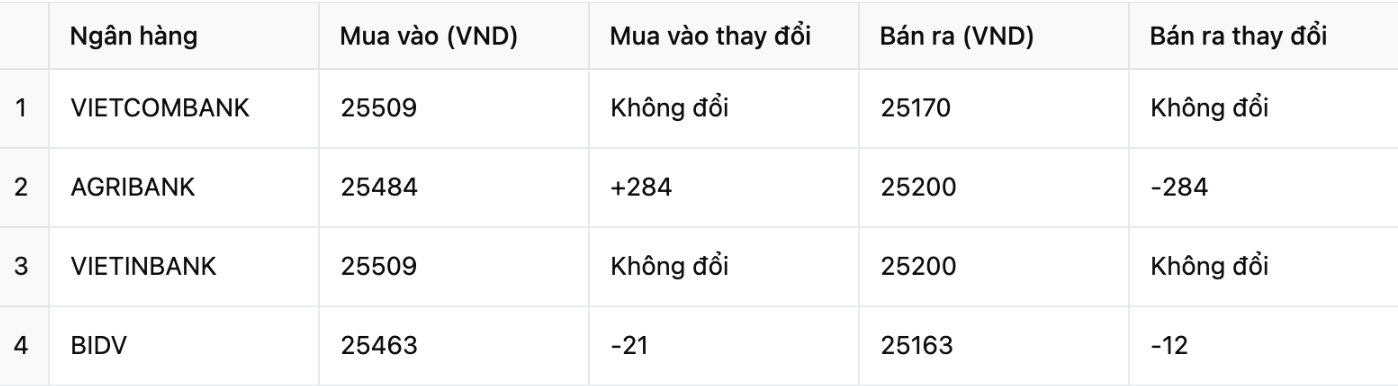
At 4 major banks (Vietcombank, VietinBank, BIDV, Agribank), the selling price of USD decreased sharply, except for Vietinbank and Vietcombank which remained unchanged in both directions compared to yesterday's session.
Vietcombank: USD exchange rate remains unchanged in both directions, listed at selling price of 25,170 VND and buying price of 25,509 VND.
Agribank: The USD fell sharply by 284 VND in the selling direction to 25,200 VND. Meanwhile, the buying direction increased by 284 VND compared to the previous trading session, currently anchored at 25,484 VND.
BIDV: USD/VND exchange rate decreased by 12 VND for selling and 21 VND for buying, down to 25,163 VND and 25,463 VND respectively.
VietinBank: No change recorded, USD selling price remains at 25,200 VND and buying price at 25,509 VND.
In the world market, the DXY index - the US Dollar Index (DXY) measuring the greenback's fluctuations against six major currencies (EUR, JPY, GBP, CAD, SEK, CHF), touched 106.21 at one point in the last trading session, after falling to a low of 105.85 in the previous session, a two-week low.
Michael Brown, senior research strategist at Pepperstone, expects the dollar to recover early next month.
What factors affect the USD?
The US dollar is one of the most important currencies in the world, the value of which is often affected by many economic, political, and financial factors.
Monetary policy of the US Federal Reserve (Fed)
When the US Federal Reserve (Fed) raises interest rates, the USD tends to strengthen as investors seek higher yields. Conversely, when the Fed cuts interest rates, the USD tends to weaken.
The dollar is also dependent on quantitative easing (QE). Printing more money to stimulate the economy can devalue the dollar.
Political and geopolitical situation
The USD is considered a safe haven, so it often appreciates when there is instability in other parts of the world. At the same time, US trade policies, tariffs, and trade agreements with other countries also affect the USD.
Trade balance
When the US imports more than it exports (trade deficit), the demand for USD can decrease, leading to a weakening of the currency.
Oil and commodity price fluctuations
Oil is priced in USD on the international market. When oil prices rise or fall sharply, this can affect the value of the USD.
Health of the US economy
When the US economy is growing strongly, the USD usually appreciates. Additionally, low unemployment and positive job growth can strengthen the USD.
Inflation is also one of the factors that cause fluctuations in the USD. If the inflation rate remains stable, it can support the USD, but if it is too high, it can cause concerns about the purchasing power of the currency.











