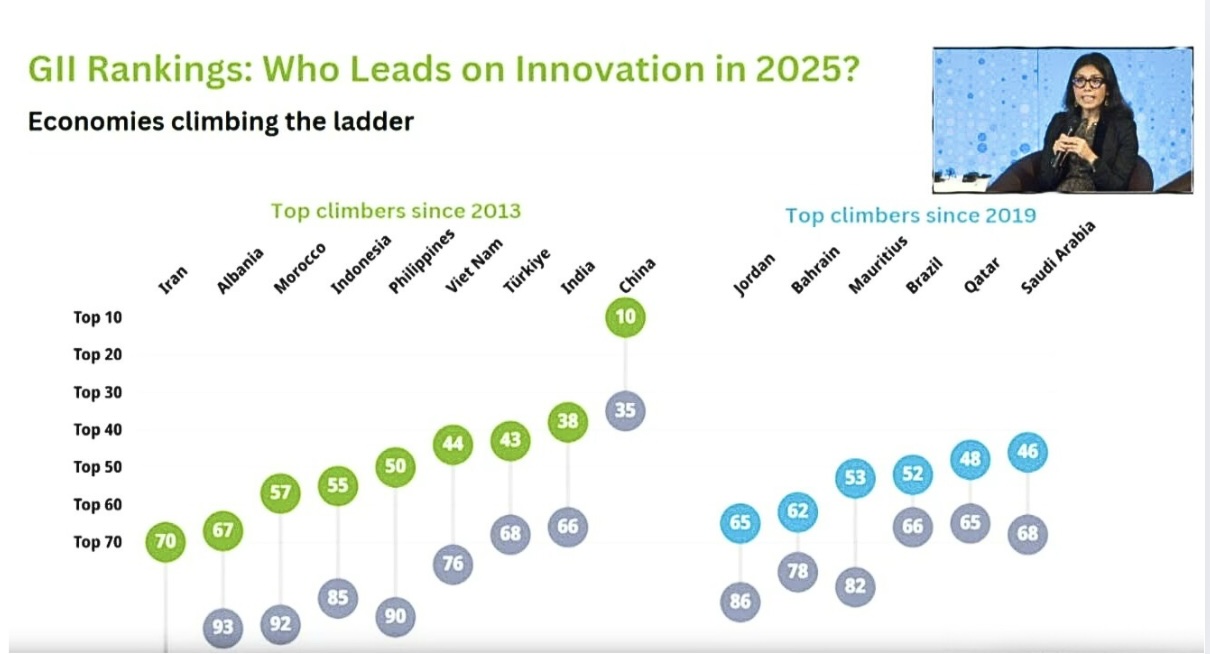
In this report, Vietnam was recognized by WIPO as one of the nine middle-income countries with the fastest improvement in ranking since 2013, along with China, India, Turkey, the Philippines, Indonesia, Morocco, Albania and Iran.
At the same time, Vietnam is also one of two countries to hold the record of 15 consecutive years with outstanding achievements over the development level, demonstrating the ability to turn input resources into output results much more effectively than many countries with the same level of development. The report also shows that Vietnam is in the group of three countries with the fastest labor productivity growth rate in the period of 2014-2024, along with China and Ethiopia.
In the innovation input group, Vietnam has increased three places compared to 2023, from 53rd to 50th. Input is evaluated based on five pillars: institutions, human resources and research, infrastructure, market development level and business development level.
Some indicators have improved significantly, such as the stability of policies and regulations related to the business environment, the level of diversity in domestic production or the effectiveness of law enforcement. This is considered a foundation for improving competitiveness and attracting investment.
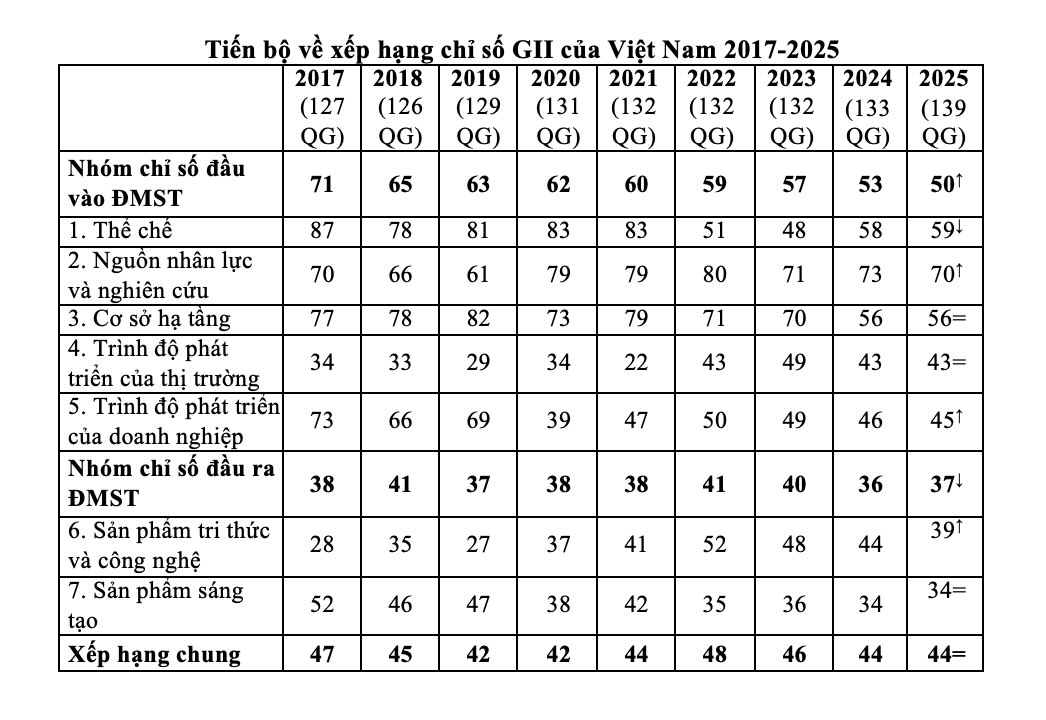
With innovation output, Vietnam ranked 37th, down one place compared to 2024, but still had many notable bright spots. For the first time, Vietnam has become the world leader in creative goods exports, while continuing to maintain its leading position in high-tech imports and high-tech exports.
indices such as labor productivity growth rate (ranked 4th), number of smartphone applications created (ranked 7th) or the part spent on research and development covered by enterprises (ranked 8th) also showed a clear improvement.
However, the report also frankly pointed out many obstacles that hinder Vietnam's development process. Education is still a weakness when the expenditure rate for education decreased by 10 places (at 116), while the ability to attract international students has not improved.
In digital infrastructure, the index of access and use of information technology tends to decrease. In terms of ecological sustainability, energy efficiency and the ratio of low-emission energy sources have decreased significantly. In addition, the ability to absorb knowledge and innovate in services has not achieved positive results when importing ICT services, exporting ICT services or copyright money are all low.
In the ASEAN region, Vietnam maintained its third position, only behind Singapore and Malaysia, and surpassed Thailand. In the group of lower-middle-income countries, Vietnam ranks second, only behind India.
It should be noted that the data used for assessment in GII 2025 is calculated for the period 2015-2024, in which many indicators are based on data from 2023. Therefore, the major policies of the Party issued in recent resolutions along with the strong changes from the end of 2024 to now are expected to be more clearly reflected in the following reporting periods.











