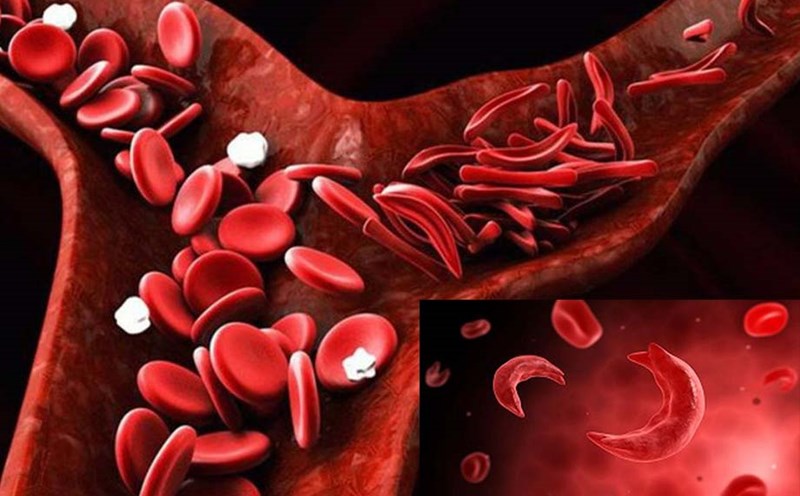
In food, iron exists in two main forms:
Heme iron (found in meat, fish, eggs) - easy to absorb.
Non-heme iron (found in plants) - absorbed less but may increase when combined with vitamin C.
Here are 5 iron-rich vegetables that help supplement this important nutrient naturally.
Spinach (Steddy Spinach)
Spinach is one of the most rich in iron. According to the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA), 100g of spinach contains about 2.7mg of iron, meeting nearly 15% of daily needs.
This vegetable also contains vitamin C, folate and antioxidants, which help the body absorb iron better. A study from the British Journal of Nutrition (British Journal of Nutrition) shows that combining spinach with foods rich in vitamin C such as lemon, bell peppers or tomatoes will increase the absorption of iron.
steamed or lightly stir-fried spinach should be eaten instead of boiled for too long to preserve nutrition.
Kale
Kale is a leafy green vegetable that contains many nutrients, in which 100g of kale contains about 1.5mg of iron. In addition, it also contains vitamins K, C and calcium, which help support bone and joint health and the immune system.
According to research from the US Institute of Nutrition & Food (AND), kale is rich in polyphenols that help reduce inflammation and increase iron absorption, especially in people with a vegan diet.
Can be processed into salads, juices or lightly stir-fried with olive oil for better absorption.
Broccoli
Broccoli not only contains 1mg of iron/100g but is also rich in vitamin C, which significantly improves the ability to absorb iron.
According to research from the American Dietetic Association (ADA), broccoli provides 168% of daily vitamin C needs in just one serving, helping the body absorb iron more effectively than other vegetables.
Broccoli also contains sulforaphane a plant compound that helps reduce inflammation and protect the heart.
Squeeze or lightly stir-fry broccoli with vegetable oil to increase nutrient absorption.
Amaranth
Amaranth contains about 2.5mg of iron/100g, on par with spinach, which helps increase red blood cell production and prevent anemia.
According to the Journal of Food Science & Nutrition (FNS), amaranth also contains a lot of calcium, magnesium and vitamin A, which help strengthen the immune system and protect the eyes.
Research from the National Institute of Nutrition in India shows that red amaranth is especially rich in antioxidants, which have the effect of preventing inflammation and improving blood circulation.
Amaranth soup with shrimp can be cooked or eaten with foods rich in vitamin C to increase iron absorption.
Asparagus
Asparagus is a vegetable rich in iron with 1.5mg of iron/100g, and also contains a lot of fiber, folate and prebiotics, which help support digestion and improve intestinal bacteria.
According to research from the European Journal of Nutrition & Metabolism (EJNM), folate in asparagus helps the body synthesize red blood cells and prevent anemia.
You can steam or lightly stir-fry with olive oil to retain the nutrients.