Difficulty breathing after mild exercise signals health risks
According to Dr. Divya Bansal, clinical hematologist and BMT, Manipal Dwarka Hospital, New Delhi (India), shortness of breath after exercise is one of the symptoms that many people can ignore, but in fact, , that may be a sign of anemia, especially sickle cell anemia (SCA).
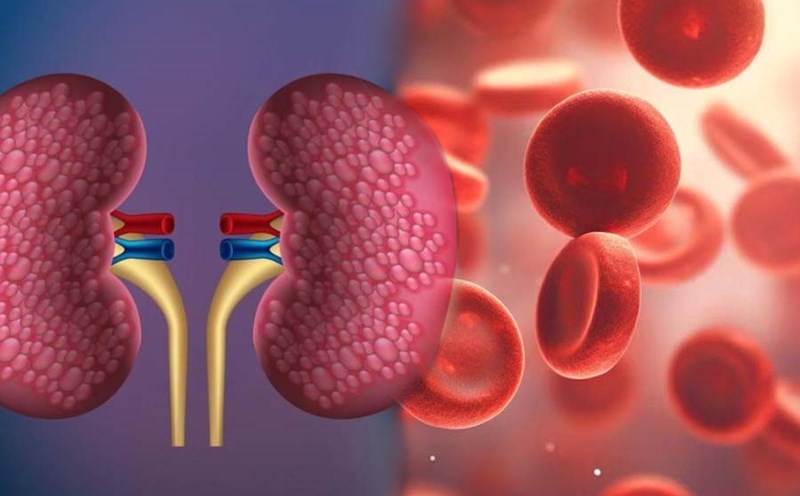
Sickle cell anemia is a genetic disorder of blood, in which red blood cells have no normal shape, making it difficult to transport oxygen to tissues and organs in the body.
After you exercise lightly but feel difficult to breathe, this may be a sign of a hidden health problem, especially when the amount of hemoglobin in the blood is low. In particular, red blood cells have abnormal shapes, making the process of oxygen in the body difficult.
Typically, red blood cells have a circular shape, which helps to transport oxygen easily through blood vessels. However, in sickle cell anemia, these cells are shaped like a sickle, hindering blood circulation and reducing the ability to provide oxygen to parts of the body. Therefore, patients may feel difficulty breathing, especially when exercising, because the body does not receive enough oxygen.
Symptoms of shortness of breath can come with a more serious condition called acute breast syndrome, this is a life -threatening complication if not treated promptly.
Other symptoms of the disease
Dr. Divya Bansal said that in addition to shortness of breath, sickle cell anemia also causes a series of other serious symptoms, including:
Relapse: Pain may occur when blood flow is hindered, affecting any part of the body. In particular, the pain usually occurs in the chest, abdomen or joints.
Fatigue: Because red blood cells cannot transport oxygen effectively, patients often feel tired and weak, even chronic fatigue.
Lower respiratory infections (LRTI): Due to weakened immune system, patients with sickle cell anemia susceptible to pulmonary infections, affecting the ability to resist pathogens.
The risk of stroke: The severity of the sickle cell anemia increases the risk of stroke, especially in young patients, because the supply of oxygen to the brain is impaired.