Environmental conditions
Cold weather and low humidity reduce the skin's ability to retain moisture, contributing to dry skin, including the skin between fingers.
tiep xuc allergy amoeba
tiep xuc allergy (also known as Dyshidrosis) is one of the common causes of dry skin between fingers. Symptoms often appear in the soles of the feet, palms and the sides of the fingers. This chronic dermatitis is characterized by small, fluid-filled blisters, which can be very itchy. These blisters can rupture, causing cracking, peeling, and dry skin.
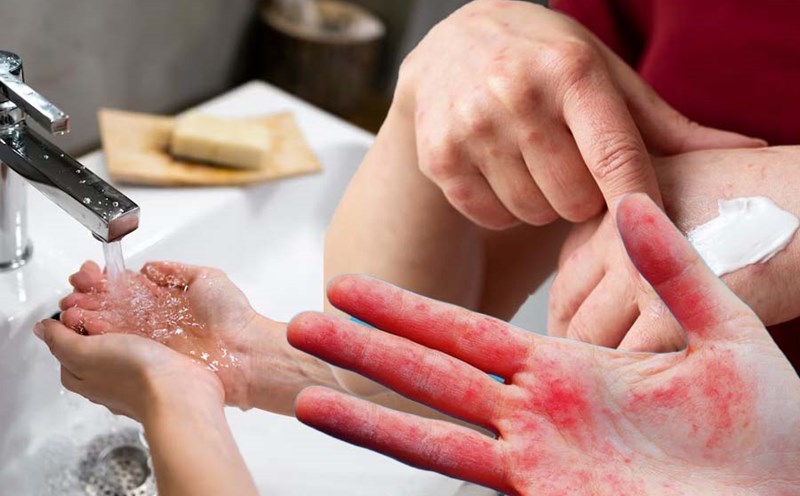
Wash your hands regularly
Wash your hands regularly with soap or an alcoholic disinfectant that removes the skin's natural oils, causing redness and dry skin. Components such as sodium lauryl sulfat, alcohol (ethanol), paraben and artificial fragrances in soap can break down the skin barrier, leading to dry skin between the fingers.
Mushroom infections
When the body is infected with fungi such as hand markers, the skin breaks down the protective barrier, causing dryness, peeling and cracking.
Vitamin A deficiency
Vitamin A deficiency affects cell regeneration and sebum production, causing dry skin and peeling. Vitamin A is a fat-soluble micronutrient that is essential for the skin.