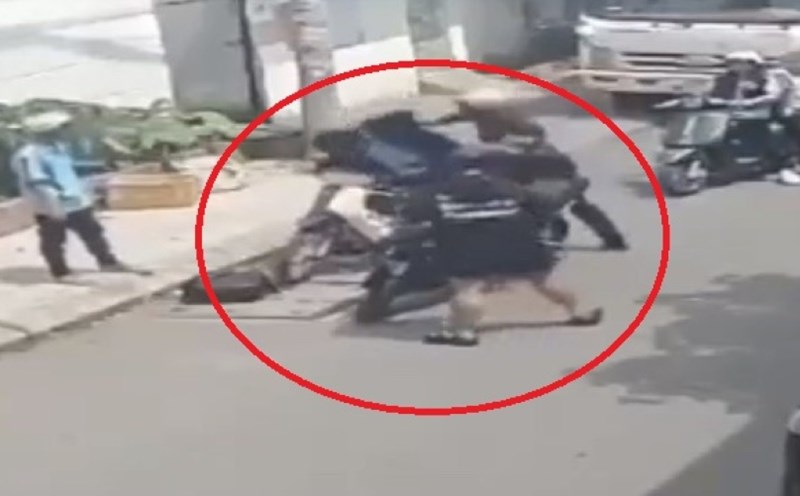
Encrusted soybeans are rich in protein
Tempeh provides 18 grams of protein/85 g, rich in beneficial bacteria for the intestines. Tempeh is both protein-rich and aids digestion and mineral absorption, making it ideal for vegetarians or those who want to lose meat, says nutritionist Lauren Panoff, Director of the American Center for Plant Nutrition.
Seitan, wheat gluten instead of meat
Seitan contains 15 g of protein/85 g, has a tough texture like meat, suitable for cooking salty dishes. However, people with gluten intolerance should limit it.
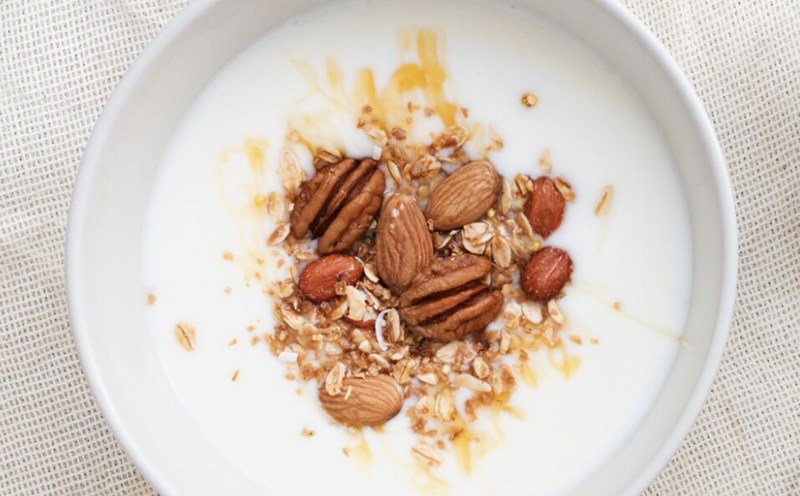
Oatmeal - a nutritious breakfast
Oatmeal provides 11 grams of protein/85 g, rich in fiber and beta-glucan to support the heart and digestion. Can be combined with chia seeds, flax seeds or nut butter to increase protein.
Soybeans - complete protein
Soybeans contain 10 grams of protein/85 g, rich in all 9 essential amino acids, helping to ensure comprehensive nutrition.
Flexible tofu, easy to prepare
Tofu provides 8.5 g of protein/85 g, suitable for cooking stir-fried dishes, curries or eating raw with soy sauce and spices.
Lentils add fiber and iron
Lentils contain 8 grams of protein/85 g, cooked quickly, easy to eat in soups, salads or stews.
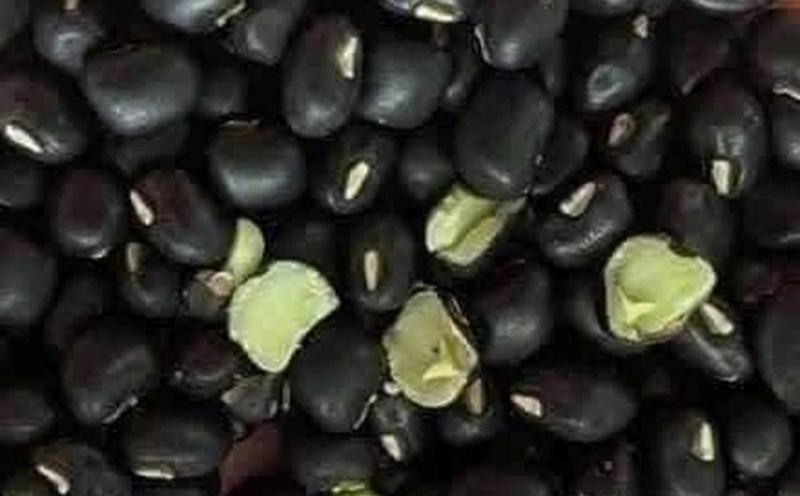
Black beans are nutritious and easy to find
Black beans provide 6 grams of protein/85 g, and are rich in antioxidants and fiber, making them suitable for soups, salads or stir-fried dishes.
Chickpeas - cheap and versatile protein
Chickpeas also contain 6 grams of protein/85 g, a popular ingredient in hummus, salads or stews, easy to incorporate into your daily diet.
How to supplement plant protein during the day
Breakfast: oatmeal mixed with chia seeds, soy milk smoothie, chickpea flour pancakes.
Lunch: Chickpea salad, lentil soup, deep-fried pitafel bread.
Dinner: tofu curry, stir-fried with green vegetables, burrito lentils and quinoa.
Snack: mixed nuts, soy yogurt, hummus with vegetables.