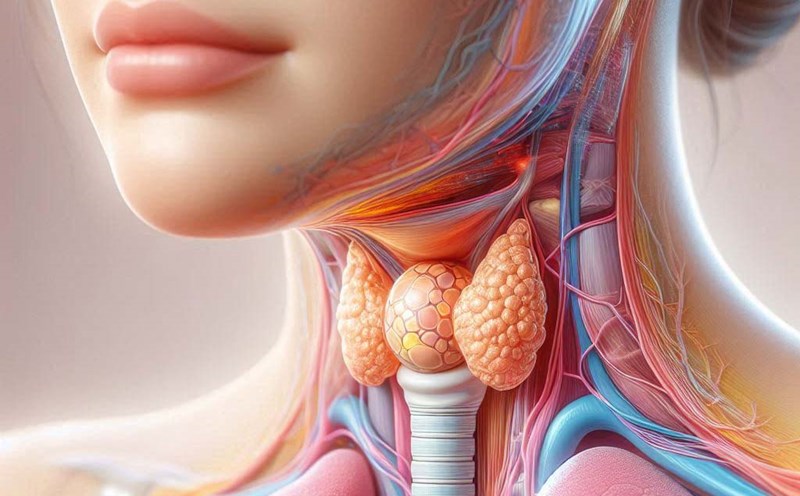
Hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism
Dr Sangeeta Anand, obstetrician at Apollo Fertility Brookfield Hospital (India) – said that the thyroid gland produces important hormones to regulate various functions of the body, including metabolism, mood and fertility.
When thyroid function is impaired, especially in the case of hypothyroidism, it can significantly affect fertility.
Agreeing, Dr. Kalyani Shrimali, obstetrician and gynecologist at Nova IVF Fertility (Indore, India) - further affirmed that both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism can affect fertility.
Hypothyroidism can lead to irregular periods, failure to ovulate, and difficulty conceiving, while hyperthyroidism can disrupt the menstrual cycle and increase the risk of miscarriage.
The link between thyroid and fertility
Thyroid hormones and reproduction: Thyroid hormones affect the menstrual cycle, ovulation, and growth of the uterine lining.
An imbalance in thyroid hormones can disrupt these processes, leading to irregular menstrual cycles, failure to ovulate, and altered uterine function.
Endometriosis: Hypothyroidism is common in women with endometriosis, a condition that can also cause fertility problems.
Decreased libido: Hypothyroidism can cause decreased libido, making couples less likely to have sex regularly.
Miscarriage: Women with hypothyroidism are more likely to have miscarriages, especially if their thyroid function is not well controlled.
Anovulation: Anovulation is common in women with hypothyroidism. If you can't ovulate, it means you can't conceive.