Hiding for millions of years under the northern rainforest, a sudden geological fault has returned with the risk of causing a catastrophic earthquake from Alaska to Montana and Canada.
According to the latest warning from scientists at the University of Victoria ( British Columbia, Canada), the Tintina fracture - a more than 1,000 km long seismic system running across the Northeast of British Columbia, crossing Yukon to Alaska - could be an underrated threat. The research work has just been published in the journal Geophysical Research Letters.
New research shows that this disruption has quietly accumulated energy for a huge earthquake, said Dr. Michael West, a district seismologist in Alaska. This is one of the least studied fractured systems in North America, and that needs to change.
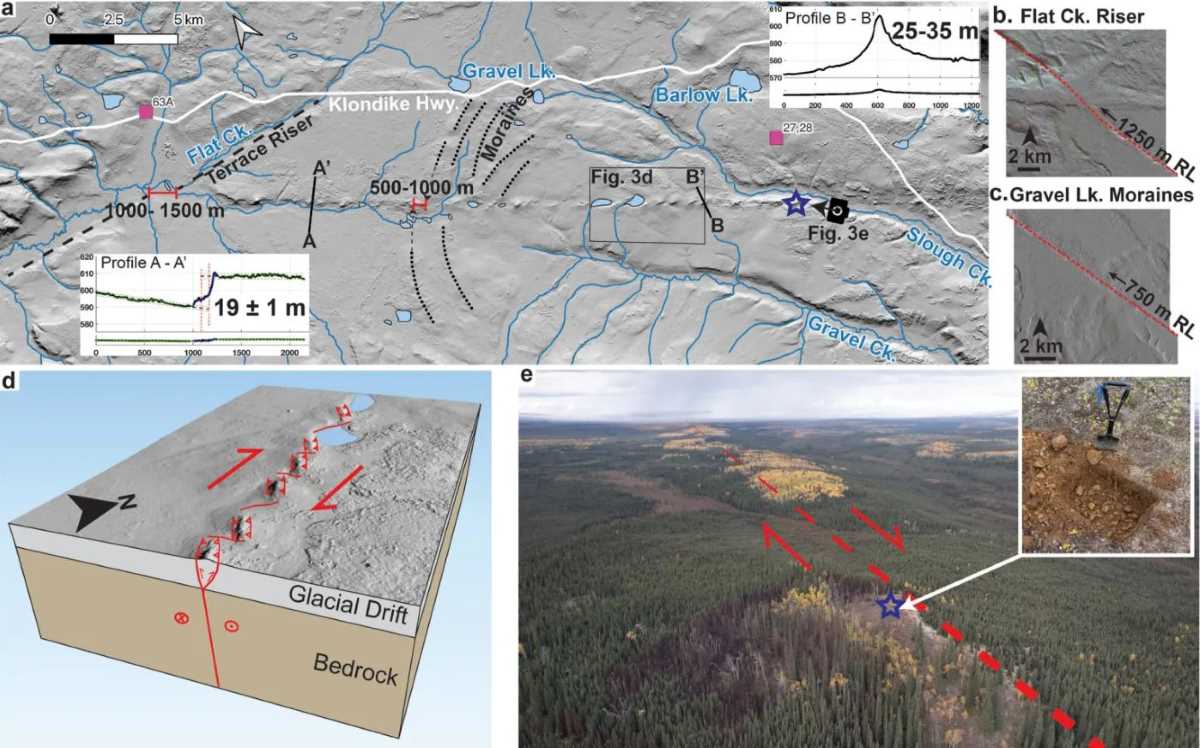
Although it has traveled as far as 450km in the past, scientists have previously thought Tintina has been inactive for 40 million years. But using terrain scanning technology from satellites, airplanes and drones, the team discovered a 130km long stretch near Dawson City, Canada, showing signs of major earthquakes in the Fourth Century - lasting from 2.6 million years to the present.
Researchers found traces of ice terrain that was skewed more than 900m ago by 2.6 million years and another section that slid more than 75m from about 135,000 years ago. More importantly, Tintina is still expanding at a rate of 0.2 to 0.8mm per year - a clear sign that geological pressure is continuing to accumulate.
If the entire area of this accumulation (6m within the past 12,000 years) is released, the earthquake could exceed 7.5 degrees richter. And that would be a disaster, warned lead author Theron Finley.
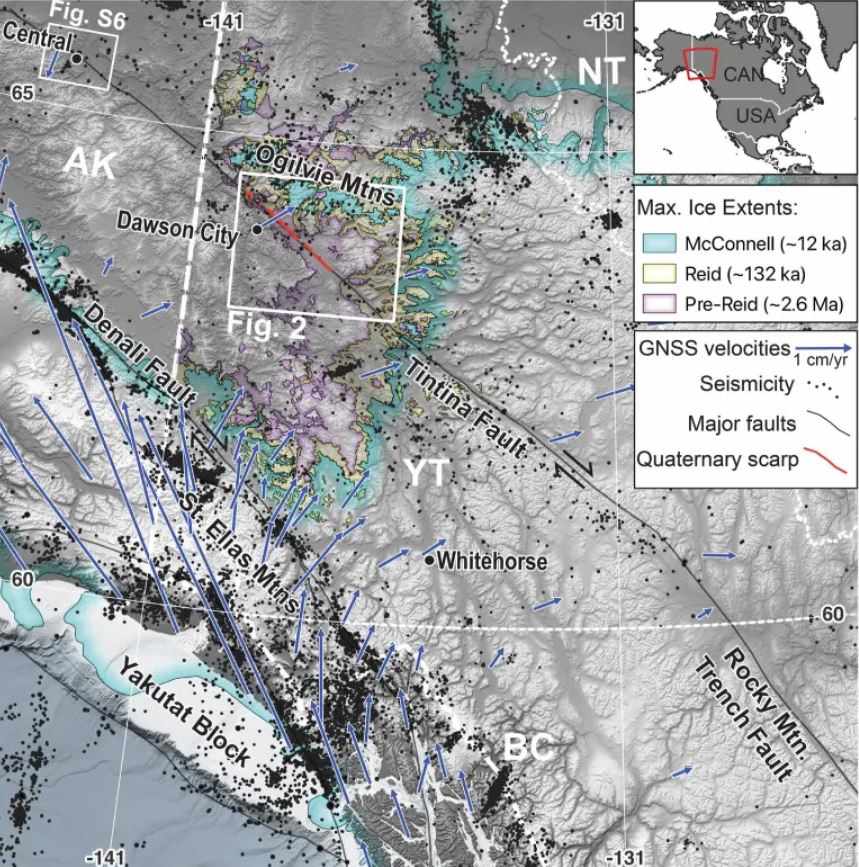
If it does, the earthquake could cause severe shaking at Dawson City, collapse roads, mines, and trigger a series of landslides. The worst scenario is a breach that could extend to Fairbanks North Star County in Alaska, affecting more than 125,000 people, and even threatening a key Trans-Alaska oil pipeline system.
Some experts even compare this situation with Hollywood disaster movies, when the aftershocks can reach as far as the state of Montana (USA).
So why has such a serious risk been "forgotten" for centuries?
The reason, according to experts, is that humans only rely on the seismic records of the past few hundred years, including documents from the modern earthquake network and local folk legends. Meanwhile, geological events that are cyclical in tens of thousands of years are often overlooked.
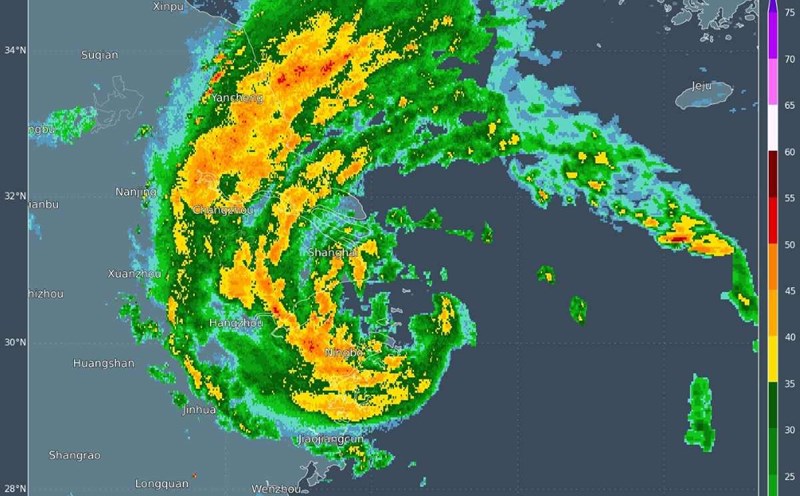
On the morning of July 30, an 8.7 term richter earthquake occurred off the coast of Russia's Kamchatka Peninsula. After the earthquake, sunny months 3-5m high hit some places in Kamchatka, the coast of Hokkaido, northern Japan, California, Alaska, Hawaii, Guam... (USA).
Many other countries such as Indonesia, the Philippines, China, Chile, Peru, Mexico, Panama... have also issued Tsunami warnings.