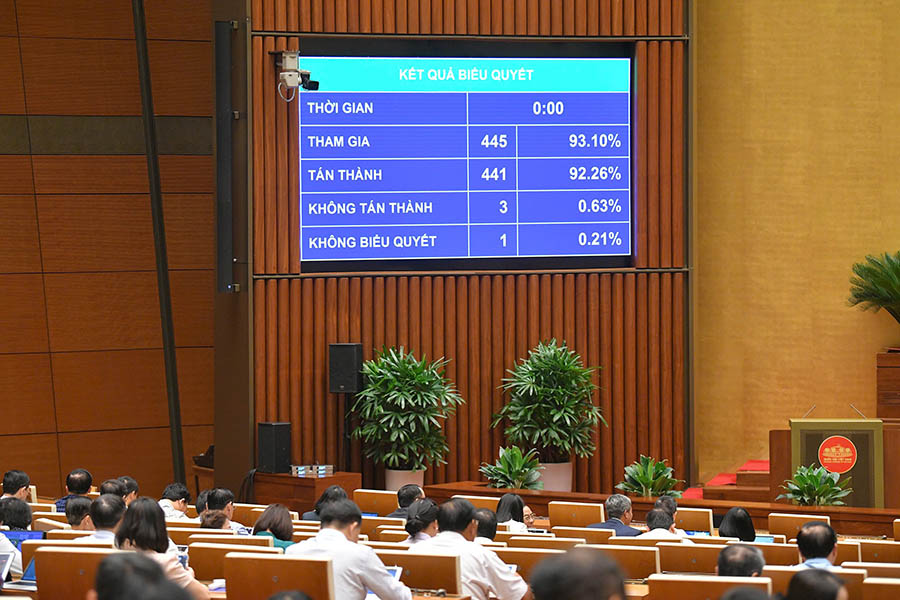
On the morning of June 14, with 441/445 delegates present in agreement, the National Assembly passed the Law on Digital Technology Industry.
The Law on Digital Technology Industry (DIT) consists of 6 chapters and 51 articles, removing 6 articles from the draft Law submitted to the National Assembly on May 9, 2025.
In particular, policies on developing digital technology human resources, artificial intelligence and the legal framework for digital asset management are outstanding contents stipulated in the Law.
Regarding attracting high-quality CNCNS human resources, Article 19 clearly states that high-quality CNCNS human resources are Vietnamese people, overseas Vietnamese people, and foreigners who meet the criteria prescribed by the Government.
High-quality CNCNS human resources are foreigners granted temporary residence cards for a period of 5 years and are extended according to the provisions of law on entry, exit, transit, and residence of foreigners in Vietnam.
Husbands or wives, children under 18 years old of high-quality CNCNS human resources who are foreigners are granted temporary residence cards with a term corresponding to the term of issuance of high-quality digital technology human resources; are facilitated and supported in procedures when looking for jobs and enrolling and studying at educational and training institutions in Vietnam.
High-quality CNCNS human resources enjoy personal income tax incentives according to the provisions of the law on personal income tax.
Regarding the principles of developing, providing, and implementing the use of artificial intelligence, the Law clearly stipulates that the development, supply, and implementation of the use of artificial intelligence must serve the prosperity and happiness of people, take people as the center, improve productivity, work efficiency, and promote intelligence;
Inclusive, flexible, fair and non-discriminatory approach; respect for moral and ethnic values; human rights, civil rights, legitimate rights and interests of organizations and individuals.
At the same time, it is necessary to ensure transparency, accountability, and explainability; ensure that it does not go beyond human control; ensure network safety and security; ensure compliance with legal regulations on data, and protect personal data;
Ensure the ability to control artificial intelligence algorithms and models; control risks throughout the life cycle of the artificial intelligence system; ensure compliance with laws on consumer rights protection and other relevant laws.
Regarding digital assets, the Law identifies them as a form of property according to current civil law. However, instead of issuing a separate law, the CNCNS Law approaches in a general principle direction, and assigns the Government to specify in detail the contents of digital asset management according to practice and development needs.
In which, Clause 1, Article 49 clearly states that the management contents include: creating, issuing, transferring, establishing the right to own digital assets; rights and obligations of parties participating in related activities; ensuring information security, network security; preventing and combating money laundering, terrorist financing...
In particular, the draft law requires control of all business activities of digital asset services, including cryptocurrency assets.
The National Assembly Standing Committee believes that this approach will ensure flexibility, feasibility and compliance with international practices, while laying the foundation for effective digital asset management in the coming time.
The CNCNS Law takes effect from January 1, 2026.
Some regulations on finance for the development of the digital technology industry; support and investment incentives for product production, digital technology service provision; support for creative startup projects in the digital technology industry effective from July 1, 2025.











