On February 2 Eastern time, President Donald Trump signed a decree on global countervailing tax on all goods entering the US, and raised the tax rate for more than 60 countries and territories.
President Donald Trump announced a 10% import tax on all imports into the US for all countries and territories, from April 5, 2025.
Then, from April 9. In 2025, more than 60 countries and territories, the US's largest trading partner, will be subject to counterpart tariffs at a higher level.
The US Trade Representative Office announces the counterpart tax calculation method as follows:
Summary
Countervailing tax is calculated based on the tax rate needed to balance bilateral trade deficits between the US and each trade partner. This calculation assumes that the long-term trade deficit is due to a combination of tariff and non-tax factors, which hinder trade balance. Taxes have a direct impact on import reduction.
The counterpart tax rate ranges from 0% to 99%, with the average weightless rate of 20% and the average weight according to import value of 41%.
Calculation method
Consider a model in which the US applies the τi rate to the country and the Δi is a change in the tax rate.
ε<0 is the expansion of imports according to import prices.
φ>0 is the level of tariff transmission to import prices.
mi>0 is the total import value from country i
xi>0 is the total export value.
Import volumes reduced by tariff changes are calculated according to the Δτi x ε x mi <0 Assuming the impact of exchange rates and overall balance is insignificant, the counterpart tax rate needed to bring the bilateral trade balance to zero is calculated according to the following formula:
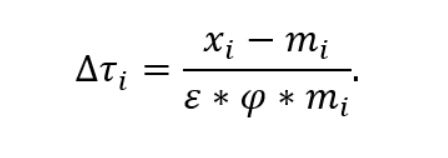
Results
The counterpart tax rate is cut to a minimum of 0% to avoid negative values. However, a higher minimum may be needed to limit the large gap between tax rates and prevent commercial transfers.
The countervailing tariff range ranges from 0% to 99%.
On average, the weightlessness of countries with trade deficits with the US is 50%.
The global weightless average is 20%.
On average, the weighting by import value of countries with a trade deficit is 45%.
The average weight globally is 41%.
The standard deviation ranges from 20.5% to 31.8%.











